Mpox Outbreak in Africa: A Growing Concern
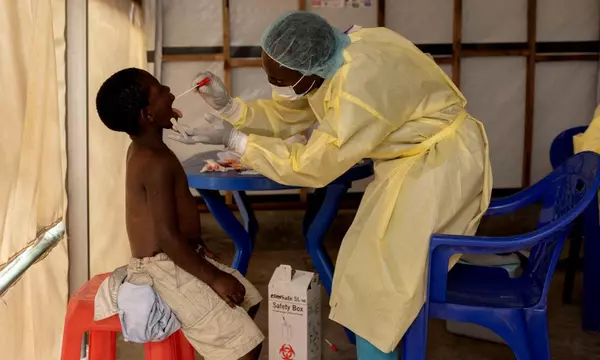
A recent mpox outbreak in Africa has escalated into a major public health crisis, leading the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) to declare a “public health emergency of continental security.” The rapid spread of the disease from the Democratic Republic of Congo to neighboring countries has raised alarm across the continent.
Understanding Mpox
Mpox is a viral infection characterized by flu-like symptoms and pus-filled skin lesions. Although most cases are mild, the disease can sometimes be severe or even fatal. The virus, which has been endemic in parts of Africa for decades, was first identified in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The Current Outbreak
The latest outbreak in Congo initially involved the endemic strain of the virus, known as Clade I. However, a new variant, Clade Ib, has emerged and appears to spread more easily through routine close contact, particularly among children. This variant has heightened concerns due to its potential for rapid transmission.
An Alarming Rate of Spread
The Africa CDC has expressed deep concern about the swift spread of the virus. The organization reported over 15,000 mpox cases and 461 deaths across the continent this year, marking a 160% increase compared to the same period last year. This surge in cases underscores the urgency for immediate and coordinated efforts to curb further transmission.
Global Response and Vigilance
In 2022, a milder version of the mpox virus spread to over a hundred countries, primarily through sexual contact, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare a public health emergency of international concern. The WHO ended this emergency after ten months, citing improved control of the health crisis. However, the ongoing outbreak in Africa serves as a stark reminder that vigilance and action are still necessary to prevent the spread of the disease.
Conclusion
The declaration of a public health emergency by the Africa CDC highlights the severity of the mpox outbreak in Africa. The rapid spread of the disease, particularly among children, is a significant concern. To prevent further transmission and mitigate the impact of the outbreak, governments, health organizations, and individuals must work together, particularly in high-risk areas. Proactive measures are crucial to controlling the outbreak and safeguarding public health across the continent.


